Table of Contents
- Summary
- What are Fibroids?
- Types of Fibroids
- Symptoms of Fibroids
- Fertility- and Pregnancy-Related Concerns
- Examples of Pregnancy Concerns
- Malpresentation of a Fetus
- Preterm Labour
- Labour Dystocia
- Postpartum Hemorrhage
- Pain
- Pregnancy with Fibroids
- Understanding Fibroids and Their Impact
Summary:
- Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors of the uterus, affecting up to 70% of women, with many experiencing no symptoms.
- There are four main types of fibroids based on their location: pedunculated, subserosal, submucosal, and intramural. Each type affects the body differently.
- Symptoms of fibroids can include abnormal uterine bleeding, pelvic pressure, constipation, pain during intercourse, and fertility concerns such as difficulty conceiving or miscarriage.
- Fibroids may also impact pregnancy, potentially leading to complications like preterm labour, labour dystocia, malpresentation, and postpartum hemorrhage, making medical guidance essential.
Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors in the uterus, affecting up to 70% of women. While some cause no symptoms, others can lead to issues like abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and discomfort. In addition to physical symptoms, fibroids can sometimes affect fertility and pregnancy, potentially leading to complications such as miscarriage, preterm labour, malpresentation, or postpartum hemorrhage. However, many fibroids themselves are harmless, and proper medical guidance can help manage any concerns related to fertility or pregnancy.
What are Fibroids?
Fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) tumors of the smooth muscle of the uterus. Up to 70% of women have fibroids. Some fibroids are small and people don’t even know they have them because they have no symptoms. Other fibroids can cause significant symptoms.
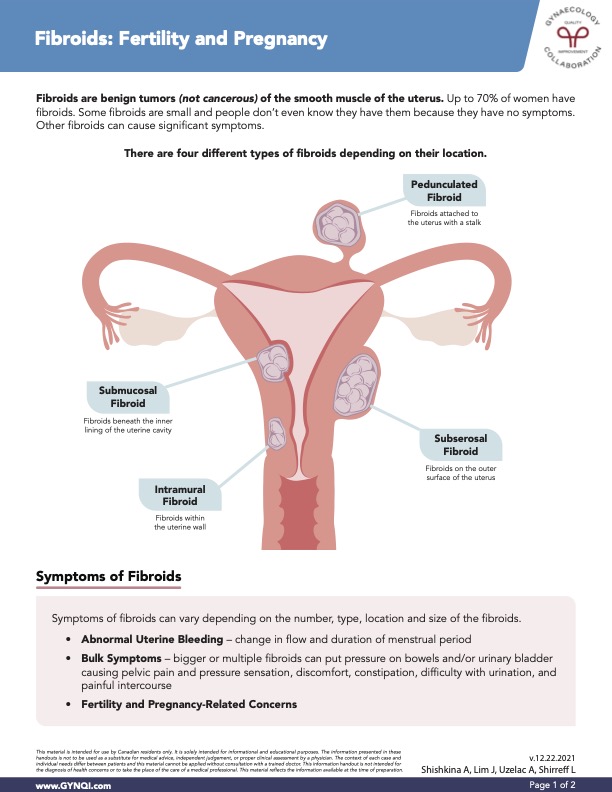
Types of Fibroids
Depending on their location, there are four different types of fibroids. These are:
- Pedunculated Fibroids: Fibroids attached to the uterus with a stalk
- Subserosal Fibroids: Fibroids on the outer surface of the uterus
- Submucosal Fibroids: Fibroids beneath the inner lining of the uterine cavity
- Intramural Fibroids: Fibroids within the uterine wall
Symptoms of Fibroids
Symptoms of fibroids can vary depending on the number, type, location, and size of the fibroids.
Symptoms can include:
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Change in flow and duration of menstrual period
- Bulk Symptoms: Bigger or multiple fibroids can put pressure on the bowels and/or the urinary bladder causing pelvic pain and pressure sensation, discomfort, constipation, difficulty with urination, and pain during intercourse
- Fertility- and pregnancy-related concerns
Fertility- and Pregnancy-Related Concerns
Fibroids, though common, can sometimes raise concerns about fertility, making it important to understand how they might impact your reproductive health.
Infertility: Depending on the size and location of fibroids, some fibroids can distort the uterine cavity and ultimately lead to difficulties getting pregnant.
Miscarriage: When fibroids distort the uterine cavity, there can be instances where it is more challenging for a pregnancy to continue. On occasion, this may result in a miscarriage that most commonly takes place in the first trimester.
Examples of Pregnancy Concerns
Fibroids during pregnancy can lead to potential concerns and may affect both your health and your baby’s development. It’s important to understand their impact and to discuss your options with your doctor.
Malpresentation of a Fetus
Most babies are positioned vertex, or head down, closer to the due date, which is an ideal position for vaginal delivery. However, depending on the size and location of a fibroid, it can interfere with a baby’s positioning inside the uterus. A Caesarean section may be required for delivery.
Preterm Labour
Going into labour before 37 weeks is considered preterm, or an early birth. Depending on their size and location in the uterus, fibroids can increase the chances of preterm labour by affecting the uterus’s ability to expand properly, leading to early contractions. Understanding the potential influence of fibroids on preterm labour can help ensure closer monitoring and early intervention if needed.
Labour Dystocia
Larger fibroids that are located in the lower part of the uterus can impede the baby’s passage through the birth canal.
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Fibroids found within the uterine wall can prevent the uterus from contracting appropriately after delivery, therefore contributing to excessive bleeding immediately after giving birth.
Pain
As pregnancy progresses, the uterus grows and the architecture of the uterine wall changes, causing decreased blood flow to fibroids. Without blood supply, fibroids can degenerate causing local inflammation and pain. This is more common in the second and third trimesters.
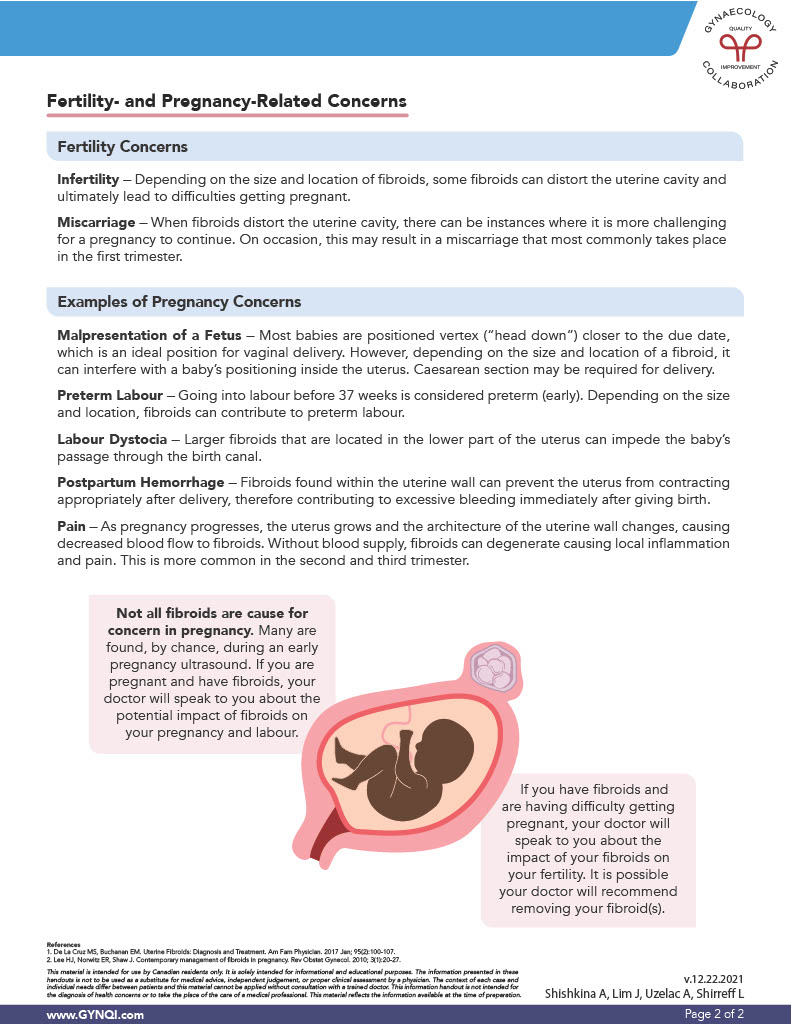
Pregnancy with Fibroids
It’s important to note that not all fibroids are a cause for concern in pregnancy. Many are found by chance during an early pregnancy ultrasound. If you are pregnant and have fibroids, your doctor will speak to you about the potential impact of fibroids on your pregnancy and labour.
If you have fibroids and are having difficulty getting pregnant, your doctor will speak to you about the impact of your fibroids on your fertility. It is possible your doctor will recommend removing them.
Understanding Fibroids and Their Impact
Fibroids are common and often go unnoticed due to a lack of symptoms, others can cause issues such as abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure. The impact of fibroids on fertility and pregnancy varies depending on their type, size, and location, and although some fibroids may contribute to infertility or pregnancy complications, others pose no concern.
If you are experiencing symptoms or have fertility concerns related to fibroids, discussing options with your doctor can help you make informed decisions about your health and treatment.