Table of Contents
- Summary
- Types of GnRH Agonists
- What are GnRH Agonists?
- How do GnRH Agonists Work?
- Are GnRH Agonists Effective?
- How Do I Take My GnRH Agonist?
- What Can I Take to Help with the “Flare Effect”?
- When Will the Medication Start to Work?
- Are the Effects of GnRH Agonists Reversible?
- What Are the Side Effects of GnRH Agonists?
- How Do I Prevent Side Effects?
- What Are the Risks of Using GnRH Agonists?
- Taking Charge of Your Gynaecological Health
Summary:
- GnRH agonists, such as Leuprolide Acetate (Lupron™) and Goserelin (Zoladex™), are injectable medications commonly prescribed in Canada for managing endometriosis symptoms. They can be administered monthly or every three months.
- These medications work by lowering estrogen levels, effectively creating a temporary menopause-like state that alleviates pelvic pain, stops heavy periods, and shrinks fibroids.
- Most patients experience lasting relief from pelvic pain, with fibroid sizes potentially reducing by up to 45% within six months. The treatment takes about 4-6 weeks to take effect, and over 90% of patients may stop menstruating after one or two cycles.
- While GnRH agonists can cause side effects like hot flashes and headaches, these can be mitigated with “add-back” hormones (estrogen and progesterone) to protect against menopause symptoms and bone density loss.
GnRH agonists, or Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone agonists, are commonly prescribed in Canada for managing endometriosis symptoms. By lowering estrogen levels, these medications help alleviate pain and slow endometrial growth. They create a temporary menopause-like state that significantly reduces estrogen, which helps alleviate pain and slow the progression of endometrial growth. Along with “add-back” hormones, understanding how to use these treatments and manage the side effects can start you on your path to better overall health.
Types of GnRH Agonists
There are two common GnRH agonists for endometriosis in Canada:
Leuprolide Acetate (Lupron™) is an injection that is injected into a muscle – typically in the thigh, arm, or buttocks. It can be given monthly or every three months.
Goserelin (Zoladex™) is an injection that goes into the fat under the skin in the abdomen. It can also be given monthly or every three months.
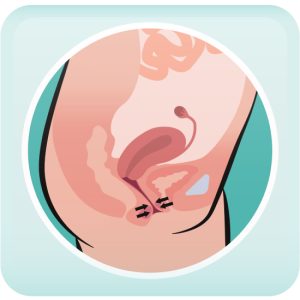
What are GnRH Agonists Used For?
GnRH agonists are used to shrink fibroids, relieve pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, and stop heavy periods, helping to improve your body’s iron levels. They can also be prescribed before surgery to allow for a less invasive procedure.
How Do GnRH Agonists Work?
GnRH agonists work by turning off the menstrual cycle and lowering estrogen levels in the body, creating a temporary menopause-like state. With reduced estrogen, the uterine lining cannot thicken, causing periods to stop. Since estrogen fuels conditions like endometriosis and fibroids, lowering its levels helps improve symptoms.
Are GnRH Agonists Effective?
Yes, they are effective! Most patients experience lasting relief from pelvic pain, and those with fibroids may see up to a 45% reduction in fibroid size within six months.
How Do I Take My GnRH Agonist?
The treatment is in the form of an injection that can be given by a nurse, doctor, or pharmacist. Your doctor might suggest starting it during your period. If it’s given during your period or the first half of your cycle, you may experience a “flare effect,” where symptoms temporarily get worse before improving.
It’s important to make sure you’re not pregnant before starting this medication.
What Can I Take to Help with the “Flare Effect”?
Talk to your doctor about prescribing a medication called Letrozole for five days after the injection to improve the symptoms from the “flare effect”.
When Will the Medication Start to Work?
The medication takes about 4-6 weeks to work, and the chance of your period stopping completely after 1 to 2 cycles is over 90%.
It is important to note that GnRH agonists do not prevent pregnancy. If you do not want to be pregnant, be sure to use a form of birth control such as condoms when having intercourse.
Are the Effects of GnRH Agonists Reversible?
The effects of the medication are temporary and completely reversible once the medication is stopped. Your regular periods will return about three months after stopping these medications.
What Are the Side Effects of GnRH Agonists?
In addition to the “flare effect”, there are a few other possible side effects of these medications.
These can include:
- Headaches
- Discomfort or redness at the site of the injection
Menopause symptoms can include:
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness
- Mood changes
- Sleep disturbance
How Do I Prevent Side Effects?
You can prevent the unwanted symptoms of menopause while still stopping your period by taking “add-back” hormones. “Add-back” is when a small amount of estrogen and progesterone hormones are added to your medication regime, and may be prescribed as a tablet to be taken by mouth, a patch, or by other routes.
Estrogen prevents symptoms, while progesterone works to protect the lining of the uterus. The doses given are not high enough to cause bleeding or pain.
Using “add-back” also helps protect your bone density.
What Are the Risks of Using GnRH Agonists?
Without “add-back” hormones, GnRH agonists can start to reduce bone density after six months. You can help support your bones by:
- Taking Vitamin D 2,000 IU daily
- Taking Calcium 1,200mg daily, either from food or supplements
- Doing weight-bearing exercise
- Decreasing alcohol intake
- Stopping smoking
Taking Charge of Your Gynaecological Well-Being
GnRH agonists are highly effective in stopping heavy periods, reducing pelvic pain from endometriosis, and shrinking fibroids. While they induce a temporary menopause-like state, this effect is fully reversible. Any menopause-related symptoms can be managed with “add-back” estrogen and progesterone, offering a balanced approach to treatment.
Speak to your doctor about how these options can help you feel your best and regain control of your health.