
Table of Contents
- Summary
- How Do Oral Progestins Work?
- Are Progestins Effective?
- Types of Oral Progestins
- What is the Difference Between Progestins and Birth Control?
- How Do I Take My Progestin?
- What if I Miss a Dose?
- What Are the Possible Side Effects?
- What Effects Do Progestins Have on Pregnancy?
- What Effects Do Progestins Have on Fertility?
- Are Progestins Safe for Long-Term Use?
- A Note About Breast Cancer
- Relief from Pain Associated with Endometriosis
Summary:
- Oral progestins reduce estrogen levels, halting the growth of endometriosis tissue and alleviating pelvic pain by preventing new blood vessel formation, which helps shrink existing lesions.
- Progestins are effective in treating endometriosis, with evidence showing that large nodules and ovarian cysts can shrink or disappear, resulting in reduced pain for many patients. However, they may not alleviate all types of pelvic pain, necessitating additional therapies like pelvic floor physiotherapy.
- The two most commonly prescribed progestins for endometriosis are Dienogest (Visanne™) and Norethindrone Acetate (Norlutate™), both taken daily. Unlike birth control pills, progestins work directly on endometriosis tissue and lower estrogen levels.
- Progestins are generally safe for long-term use but may cause side effects such as irregular bleeding, headaches, breast tenderness, hot flashes, and mood changes. They do not increase breast cancer risk but are not recommended for individuals with a personal history of breast cancer.
Oral progestins effectively treat endometriosis by reducing estrogen levels, which halts the growth of endometriosis tissue. Acting as anti-inflammatory agents, they provide significant pain relief and can shrink endometriosis nodules and ovarian cysts. Commonly prescribed progestins like Dienogest (Visanne™) and Norethindrone Acetate (Norlutate™) are taken daily, and unlike birth control pills that may worsen endometriosis due to their estrogen content, progestins directly target the condition. With proper guidance, progestins are a safe and effective long-term treatment option for managing endometriosis.
How Do Oral Progestins Work?
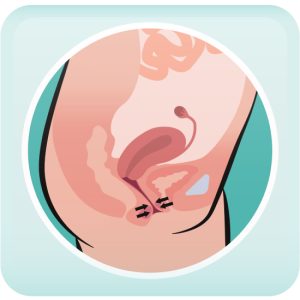
Progestins reduce estrogen, halting the growth of endometriosis tissue. As anti-inflammatory agents, they can alleviate pelvic pain by preventing new blood vessels from forming, which helps shrink endometriosis tissue.
Are Progestins Effective?
Yes, progestins are effective! Large endometriosis nodules and ovarian cysts have been shown to shrink in size or even disappear. There is great evidence that patients feel better and experience less pain.
Remember, not all pain is related to endometriosis and so a progestin may not improve all your symptoms. Sometimes other therapies, such as pelvic floor physiotherapy, may be needed.
Types of Oral Progestins
For the treatment of endometriosis, the following are the two most commonly prescribed progestins:
Dienogest (Visanne™): a 2mg pill to be taken by mouth daily.
Norethindrone Acetate (Norlutate™): a 2.5mg pill to be taken by mouth daily–your doctor may ask you to double up on this if you are tolerating it well (e.g. to take 5mg daily).
What is the Difference Between Progestins and Birth Control?
Continuous use of the birth control pill improves endometriosis symptoms in about 30% of patients. However, its estrogen content may worsen the condition in some cases.
Progestins alone work directly on the endometriosis tissue and also lower estrogen levels in the body.
How Do I Take My Progestin?
Begin this medication on the first day of your period to ensure you’re not pregnant and to reduce the likelihood of irregular bleeding. You can take the pill anytime, with or without food, but try to keep it consistent. Taking it before bed might make it easier to remember.
What if I Miss a Dose?
If you miss one or more tablets, take one pill as soon as you remember and then continue taking a pill daily at your usual time.
What Are the Possible Side Effects?
Progestins can be associated with a range of side effects that vary from mild to more severe, influencing their acceptance and usage among patients. Speak to your doctor if any side effect becomes too severe.
Irregular or Unscheduled Vaginal Bleeding: This is the most common side effect and it means the medication is working. It occurs mostly in the first 3-6 months. After six months of the medication, about one-third of patients stop having periods altogether.
Headache: This can occur in 7% of patients and is similar to a tension headache. If you have a history of migraine headaches, progestins are still safe to take.
Breast Tenderness: Some patients experience mild breast discomfort, similar to during a period.
Hot Flashes: Some patients may experience hot flashes, but these usually go away with time. This is due to the decreased estrogen in your body and it means that the medication is working.
Mood Changes: In 3-5% of patients, progestins may cause symptoms of depressed mood. If you have significant changes in your mood, please contact your doctor’s office.
Weight Gain: Progestins DO NOT cause significant weight gain.
What Effects Do Progestins Have on Pregnancy?
Visanne™ and Norlutate™ are not approved to prevent pregnancy. Since progestins block ovulation and thin the lining of your uterus, pregnancy is less likely but if you do not want to be pregnant, you should use another form of birth control, such as condoms, during intercourse.
What Effects Do Progestins Have on Fertility?
After stopping progestins, periods return to normal after one to two months, which means you can become pregnant very soon after stopping the medication. It is unclear whether progestins increase your fertility chances. Some data suggest that shrinking or preventing endometriosis may even improve fertility.
Are Progestins Safe for Long-Term Use?
Progestins are safe for long-term use, however, they can be associated with a slight decrease in bone density. Bone density returns to normal once progestin medications are stopped. You can help support your bones when on progestins by:
- Taking Vitamin D 2,000 IU daily
- Taking Calcium 1,200mg daily, either from food or supplements
- Doing weight-bearing exercise
- Decreasing alcohol
- Stopping smoking
Bone density returns to normal once progestin medications are stopped.
A Note About Breast Cancer
These medications do not increase the risk of breast cancer even if you have a family history, however, you should not take progestins if you personally have had breast cancer in the past.
Relief from Pain Associated with Endometriosis
Progestins are an effective option for managing endometriosis and alleviating its associated pain. While it is crucial to allow 3-6 months for these medications to demonstrate their full benefits, most patients find them well-tolerated after an initial adjustment period. While there are side effects associated with progestins, they are safe for long-term use. This makes progestins a valuable therapeutic choice for those seeking relief from the symptoms of endometriosis.