
Table of Contents
- Summary
- What are GnRH Agonists?
- What are GnRH Agonists Used For?
- How Do GnRH Agonists Work?
- How is Medication Administered?
- When Will the Medication Start to Work?
- Are GnRH Agonists Effective?
- What are the Side Effects of GnRH Agonists?
- How Do I Prevent Side Effects?
- What are the Potential Risks?
- Are the Effects of GnRH Agonists Reversible?
- How Much Do GnRH Agonists Cost?
- Take Action with Your Gynaecological Health
Summary:
- GnRH agonists are synthetic hormones that initially stimulate FSH and LH production but later reduce these hormone levels, effectively lowering estrogen and halting the menstrual cycle.
- These medications are commonly used to shrink fibroids, treat pelvic pain from endometriosis, stop heavy periods, and help prepare for less invasive gynaecological surgeries.
- Administered as injections, GnRH agonists take four to six weeks to work, with many patients experiencing long-lasting relief from heavy periods and fibroid shrinkage.
- Potential side effects include menopausal symptoms, but “add-back” therapy with estrogen and progesterone can help manage these while protecting your bone density.
GnRH agonists are synthetic hormones that mimic natural hormones from the hypothalamus to treat gynaecological conditions like heavy periods, fibroids, and endometriosis. These medications work to eventually lower hormone levels, offering relief from symptoms. Administered as injections, they help shrink fibroids, reduce pelvic pain, and support less invasive surgeries. If you are negatively affected by heavy periods, a GnRH agonist may give you the relief you need to feel your best.
What are GnRH Agonists?
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) agonists are synthetic hormones that stimulate the pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH), which help the ovaries to function.
With continued use, GnRH agonists lead to lower levels of FSH and LH, with reduced sex hormone production.
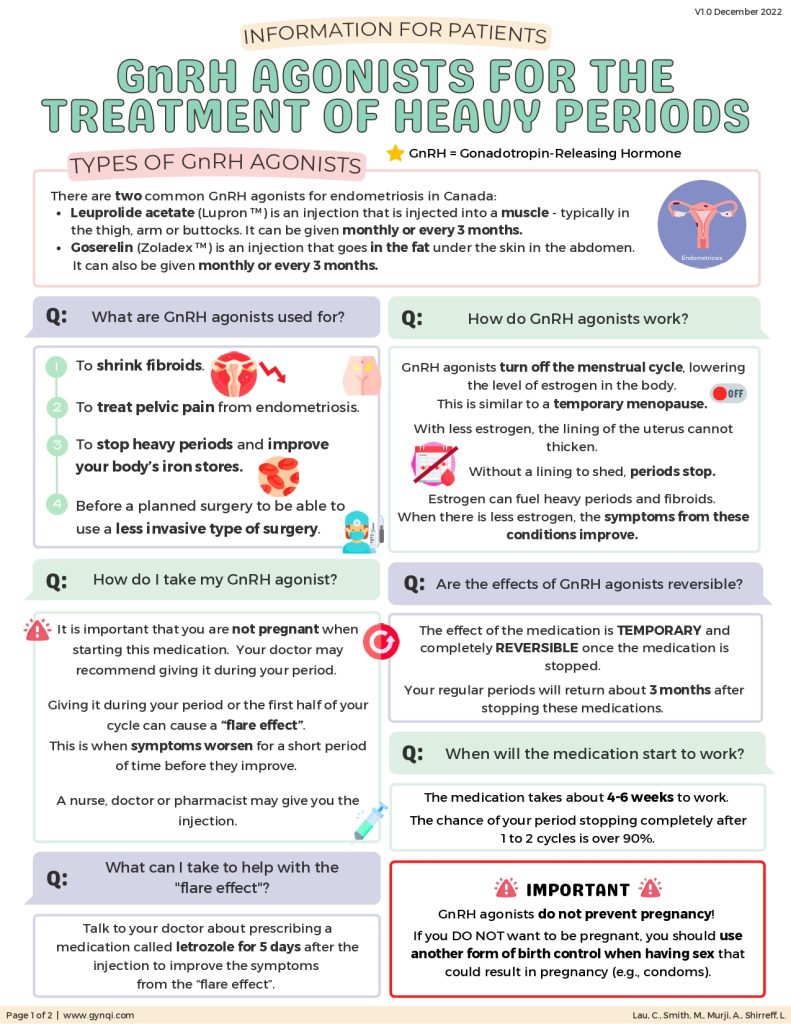
There are two types of GnRH agonists:
- Leuprolide acetate (Lupron™) is an injection that is injected into a muscle–typically in the thigh, arm, or buttocks. It can be given monthly or every three months.
- Goserelin (Zoladex™) is an injection that goes into the fat under the skin in the abdomen. It can also be given monthly or every three months.
What are GnRH Agonists Used For?
This medication has a lot of gynaecological benefits and is prescribed:
- To shrink fibroids
- To treat pelvic pain from endometriosis
- To stop heavy periods and improve your body’s iron stores
- Before a planned gynaecological surgery to be able to use a less invasive type of surgery (e.g. a laparoscopic procedure vs. an open procedure)
How Do GnRH Agonists Work?
GnRH agonists essentially “turn off” the menstrual cycle. This lowers the level of estrogen in the body, similar to a temporary menopause. With less estrogen, the lining of the uterus cannot thicken and without a lining to shed, periods stop.
Estrogen can fuel heavy periods and fibroids. When there is less estrogen, the symptoms of these conditions improve.
How is Medication Administered?
This medication is an injection, given to you by a nurse, doctor, or pharmacist.
To start, it is important that you are not pregnant when starting this medication. Your doctor may recommend giving the injection during your period.
The injection, if given during your period or the first half of your cycle, can cause a “flare effect” where your initial symptoms worsen for a short period of time before they improve. Talk to your doctor about prescribing the medication “Letrozole” for five days after the injection to improve the “flare effect” symptoms.
When Will the Medication Start to Work?
The medication takes about four to six weeks to work, with a 90% chance of your period stopping completely after one to two cycles.
It is important to note that GnRH agonists do not prevent pregnancy. Be sure to use a form of birth control (e.g. condoms) if you do not wish to be pregnant.
Are GnRH Agonists Effective?
Most patients taking this medication had long-lasting improvement with their heavy periods. Over the course of six months, patients with fibroids may notice up to a 45% decrease in fibroid size.
What are the Side Effects of GnRH Agonists?
In addition to the “flare effect”, there are a few other possible side effects associated with these medications. Side effects, including menopausal side effects, can include:
- Headaches
- Discomfort or redness at the site of the injection
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness
- Mood changes
- Sleep disturbance
How Do I Prevent Side Effects?
You can prevent the unwanted symptoms of menopause while still stopping your period by taking “add-back” hormones.
“Add-back” therapy involves taking a small dose of estrogen and progesterone, which helps prevent menopausal symptoms while protecting your uterus. The doses are low enough that they won’t cause bleeding or pain, and can be prescribed as a pill, patch, or through other methods recommended by your doctor.
What are the Potential Risks?
Without “add-back” therapy, these medications can be associated with a decrease in bone density if taken longer than months.
Incorporating “add-back” hormones will help protect your bone density, along with:
- Taking Vitamin D 2,000 IU daily
- Taking Calcium 1,200 mg daily, either from food or supplements
- Doing weight-bearing exercise
- Decreasing alcohol intake
- Stopping smoking
Are the Effects of GnRH Agonists Reversible?
The effect of the medication is temporary and completely reversible once the medication is stopped. Your regular periods will return about three months after stopping these medications.
How Much Do GnRH Agonists Cost?
GnRH agonists can be pricey, but in Canada, cost doesn’t have to be a barrier to getting the help you need. Many insurance providers and provincial drug plans offer coverage for these medications,
If you are not covered, Lupron™ and Zoladex™ offer patient support programs to help with reimbursement.
Be sure to talk to your doctor about your options.
Take Action with Your Gynaecological Health
GnRH agonists are highly effective at stopping heavy periods and shrinking fibroids by temporarily mimicking menopause. However, these effects are completely reversible once treatment ends. For those experiencing menopause-like symptoms, using “add-back” estrogen and progesterone can help manage and improve discomfort, making treatment a safer long-term option.