

Table of Contents
- Summary
- What is Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Non-Hormonal Treatment Options
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- How to Take NSAIDs for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Tranexamic Acid (TXA)
- How to Take TXA for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Hormonal Treatment Options
- Levonorgestrel Intrauterine System (LNG-IUS)
- Combined Hormonal Contraceptives (CHCs)
- Cyclic Oral Progestins
- Injected Progestins
- Danazol
- Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Agonists
- Breaking Free of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding with Effective Treatments
Summary:
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (HMB) is characterized by abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual periods, which can significantly disrupt daily activities and impact physical, social, and emotional well-being.
- Non-hormonal treatment options, such as Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and Tranexamic Acid (TXA), effectively reduce menstrual bleeding and alleviate related symptoms without hormonal intervention, allowing for personalized treatment.
- Hormonal treatments like the Levonorgestrel Intrauterine System (LNG-IUS) and combined hormonal contraceptives offer significant reductions in bleeding and menstrual pain, with varying side effects and potential impacts on fertility.
- Consulting a healthcare provider is essential for developing a tailored treatment plan for managing heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB), ensuring that individuals receive appropriate care and support to alleviate symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (HMB) is characterized by abnormally heavy or prolonged periods that disrupt daily life and affect well-being. Treatment options include non-hormonal methods such as NSAIDs and Tranexamic Acid (TXA), which reduce bleeding by 20-59%. Hormonal treatments, such as the Levonorgestrel Intrauterine System (LNG-IUS) and combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs), effectively manage HMB and may improve quality of life.
What is Heavy Menstrual Bleeding?
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding refers to abnormally heavy or longer than normal periods. It can lead to significant disruptions in people’s daily activities and overall lifestyle, impacting their physical, emotiona, and social well-being.
Non-Hormonal Treatment Options
Non-hormonal treatment options for heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) address symptoms without the use of hormones. These alternatives to hormones allow individuals to tailor their treatment to their specific needs.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), such as naproxen, ibuprofen, and mefenamic acid, have shown a 20-50% reduction in menstrual bleeding and a reduction in menstrual cramps and pain in up to 70% of patients.
NSAIDs can be used in combination with other medical treatments while awaiting further investigations into the causes of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Side effects can include:
- Indigestion
- Worsening/exacerbation of asthma
- Gastritis
- Peptic ulcers
NSAIDs have no contraceptive action, so be sure to use a form of protection during intercourse.
How to Take NSAIDs for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Start NSAIDs on the first day of your period or at the first sign of your period. You can also start NSAIDs the day before the expected start of your period.
Typical Dosing Regimens:
- Naproxen: 500mg one to two times daily
- Ibuprofen: 600 – 1200mg daily
- Mefaenamic Acid: 500mg daily
Take NSAIDs regularly for three to five days or until the bleeding stops.
Tranexamic Acid (TXA)
Tranexamic Acid (TXA) is an effective treatment option for managing heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) and can be used alongside other medical treatments while further investigations into the cause of HMB are conducted. Its primary benefit is a significant reduction in menstrual blood loss, with studies showing a 40-59% decrease in bleeding.
Side effects can include:
- Indigestion
- Diarrhea
- Headaches
- Leg cramps
TXA is not used for treating associated menstrual cramps or painful periods, and has no contraceptive action. Be sure to use protection during intercourse.
How to Take TXA for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
It is important to take TXA during your period, this is to decrease the flow.
When your period is really heavy, you can take 1g of TXA up to four times per day for up to five days per menstrual cycle. You can adjust the frequency based on your menstrual blood flow, anywhere from one to four times per day at 1g per dose.
Hormonal Treatment Options
This range of hormonal treatment options is designed to help regulate menstrual cycles and alleviate symptoms. These therapies, including hormonal contraceptives and medications, aim to reduce bleeding intensity, manage pain, and improve overall quality of life.
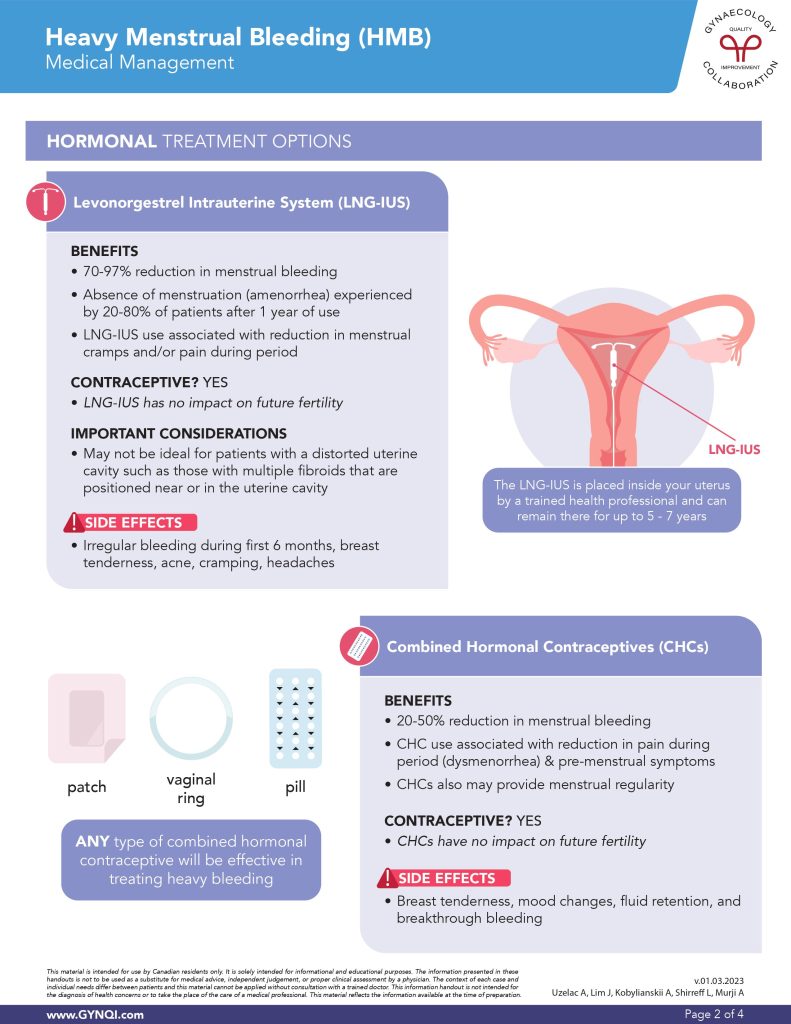
Levonorgestrel Intrauterine System (LNG-IUS)
The Levonorgestrel Intrauterine System (LNG-IUS) offers significant benefits for managing heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB), with a 70-97% reduction in menstrual blood, and the potential for 20-80% of patients to experience amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) after one year of use. Many users also report a decrease in menstrual cramps and pain.
The LNG-IUS is inserted into the uterus by a trained healthcare professional and can provide effective relief for up to five to seven years.
LNG-IUS is a form of contraceptive and has no impact on future fertility.
Side effects can include:
- Irregular bleeding duringthe first 6 months
- Breast tenderness
- Acne
- Cramping
- Headaches
This method may not be ideal for patients with a distorted uterine cavity such as those with multiple fibroids that are positioned near or in the uterine cavity.
Combined Hormonal Contraceptives (CHCs)
Combined Hormonal Contraceptives (CHCs), provided in a patch, vaginal ring, or pill form, can reduce menstrual bleeding by 20-50% and are associated with less period pain (dysmenorrhea) and pre-menstrual symptoms. CHCs also help regulate menstrual cycles, offering more consistency. Any type of CHC is effective for managing heavy menstrual bleeding, making them a versatile option for treatment.Side effects can include:
- Breast tenderness
- Mood changes
- Fluid retention
- Breakthrough bleeding
Combined Hormonal Contraceptives (CHCs) do act as a contraceptive and have no impact on future fertility.
Cyclic Oral Progestins
Oral progestin Norethisterone/Norethindrone acetate (NETA) can reduce menstrual bleeding by up to 87%. Though it is not a contraceptive, it may temporarily reduce the ability to conceive, making it potentially unsuitable for those actively trying to get pregnant.
Side effects can include:
- Breast tenderness
- Mood changes
- Bloating
- Acne
- Headaches
- Weight gain
Dosing Regimen: Norethisterone acetate (NETA) 5mg is taken three times daily for 21 days monthly (from day five to day 26 of your menstrual cycle).
Taking a lower dose of NETA for 7-11 days per month (cyclic luteal phase progestins) is not effective for treating heavy menstrual bleeding. A higher dose, taken for 21 days per month is required to manage heavy flow (long-cycle progestin).
Injected Progestins
Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) is an effective method that often leads to amenorrhea, with 60% of patients experiencing no periods within the first 12 months and 68% by 24 months. DMPA acts as a contraceptive, and there may be a delay in the return to fertility after discontinuing the treatment.
Side effects can include:
- Irregular bleeding
- Breast tenderness
- Weight gain
- Mood changes
- Decreased bone mineral density
Dosing Regimen: Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) 150mg is given as an intramuscular injection every 90 days.
Danazol
The use of this treatment can lead to an 80% reduction in menstrual bleeding, with 20% of patients experiencing no periods (amenorrhea) and another 20% experiencing infrequent periods (oligomenorrhea).
Danazol is not a contraceptive, but may not be appropriate if you’re trying to conceive.
Side effects can include:
- Weight gain
- Acne
- Muscle cramps
- Gastrointestinal upset
- Irritability
Dosing Regimen: Danazol 100-400mg taken once daily.
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Agonists
Leuprolide acetate (Lupron) and Goserelin (Zoladex) can lead to amenorrhea in up to 89% of patients within 3 to 4 weeks of the first injection, making them effective treatments for managing heavy menstrual bleeding.
These medications are not contraceptive options and may not be suitable for those trying to conceive.
Side effects can include:
- Hypoestrogenic symptoms (hot flashes, night sweats and vaginal dryness)
- Bone pain
- Loss of bone mineral density
- Mood changes
Dosing Regimen: Leuprolide Acetate (Lupron) and Goserelin (Zoladex) are both injections. Injections can be given in one-month doses or three-month doses.
When used for over 6 months, these medications may be combined with ‘add-back’ therapy, which supplements estrogen and progesterone to prevent bone density loss. This approach helps balance hormones while managing symptoms.
Breaking Free of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding with Effective Treatments
Heavy menstrual bleeding can significantly impact daily life, but various treatment options are available to help manage your symptoms effectively. Non-hormonal treatments, such as NSAIDs and Tranexamic Acid, provide alternatives that focus on reducing blood flow and alleviating discomfort. Hormonal options, including the Levonorgestrel Intrauterine System and combined hormonal contraceptives, offer substantial benefits in regulating menstrual cycles and improving the quality of life for those affected by HMB.
Speak to your doctor about a tailored treatment plan, and find relief from symptoms caused by heavy menstrual bleeding.