Table of Contents
- Summary
- What is Postmenopausal Bleeding?
- The Menstrual Cycle Before Menopause
- Bleeding After Menopause
- What Can Cause Postmenopausal Bleeding?
- Cervical Causes
- Endometrial Causes
- Vaginal Causes
- Other Causes
- Taking Action on Bleeding After Menopause
- Frequently Asked Questions
Summary:
- Postmenopausal bleeding is any vaginal bleeding that occurs more than a year after the last menstrual period, indicating the onset of menopause. This bleeding is considered abnormal and should prompt medical investigation.
- Before menopause, the uterine lining thickens each month due to estrogen from the ovaries and sheds during menstruation unless pregnancy occurs. After menopause, estrogen levels drop significantly, and the uterine lining should no longer thicken or shed.
- Various conditions can cause postmenopausal bleeding, ranging from benign issues like cervical polyps to more serious concerns such as endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. It’s essential to consult a doctor to determine the underlying cause.
- Common causes of postmenopausal bleeding include cervical and endometrial conditions, vaginal issues, uterine fibroids, cancers of the ovaries or fallopian tubes, and blood disorders. Each of these requires thorough evaluation to ensure appropriate management and treatment.
Postmenopausal bleeding refers to any vaginal bleeding occurring more than a year after a woman’s last menstrual period, indicating menopause has begun. Before menopause, the uterine lining thickens monthly due to estrogen and sheds during menstruation unless pregnancy occurs. After menopause, declining estrogen levels should prevent this thickening and shedding, making any postmenopausal bleeding abnormal and necessitating medical evaluation.
Identifying the causes of postmenopausal bleeding is crucial, as they can range from benign inconveniences to more serious health concerns.
What is Postmenopausal Bleeding?
Postmenopausal bleeding refers to any vaginal bleeding that occurs more than a year after your last menstrual period.
The Menstrual Cycle Before Menopause
Before menopause, the uterine lining (endometrium) thickens each month due to estrogen produced by the ovaries. This lining is shed during the menstrual period unless a fertilized egg implants, signaling the start of pregnancy. Regular cyclic vaginal bleeding is typical before menopause. However, during menopause, the ovaries produce significantly less estrogen, and as a result, the endometrium should no longer thicken or shed.

Bleeding After Menopause
Any bleeding that occurs after menopause is considered abnormal and warrants further investigation to rule out potential concerns related to gynaecologic structures, such as the uterus, cervix, or vagina.
It is important to note:
- Postmenopausal bleeding may not always resemble a typical menstrual period. It is important to inform your doctor about any vaginal bleeding, including spotting or discharge that appears pink or brown.
- There are many potential causes of postmenopausal bleeding, some of which may be concerning while others are not.
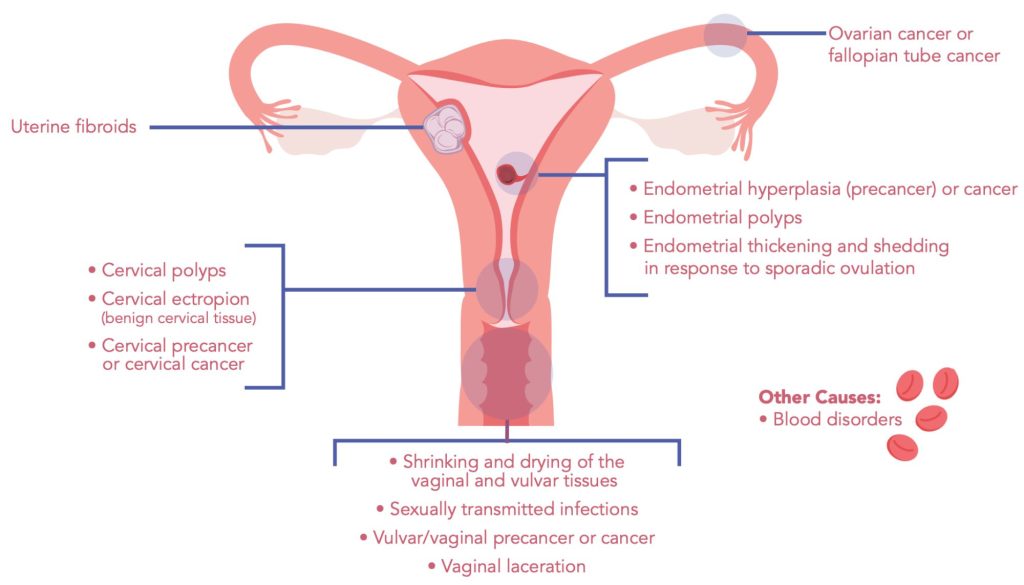
What Can Cause Postmenopausal Bleeding?
Postmenopausal bleeding can happen for many reasons, ranging from harmless conditions to more serious health concerns. It’s important to get checked by a doctor to find out what might be causing the bleeding.
Cervical Causes
Cervical causes of postmenopausal bleeding can range from benign conditions to more serious issues, making it essential to evaluate any unusual bleeding after menopause to determine the underlying cause. Causes can include:
- Cervical polyps
- Cervical ectropion (benign cervical tissue)
- Cervical precancer or cervical cancer
Endometrial Causes
Endometrial causes of postmenopausal bleeding encompasses a range of conditions affecting the uterine lining, which includes:
- Endometrial hyperplasia (precancer) or cancer
- Endometrial polyps
- Endometrial thickening and shedding
Vaginal Causes
Vaginal causes of postmenopausal bleeding can encompass a variety of conditions, from benign irritations to more serious conditions. Causes can include:
- Shrinking and drying of the vaginal and vulvar tissues
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Vulvar/vaginal precancer or cancer
- Vaginal laceration
Other Causes
Postmenopausal bleeding can also be caused by uterine fibroids, which are noncancerous growths that can lead to unusual bleeding, cancers of the ovaries or fallopian tubes, and blood disorders affecting clotting. It’s important to see a doctor for a thorough evaluation to determine the best course of action.
Taking Action on Bleeding After Menopause
Postmenopausal bleeding refers to any vaginal bleeding occurring more than a year after your last menstrual period and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. This bleeding is considered abnormal, as the menstrual cycle no longer involves shedding the uterine lining. Potential causes range from benign conditions, such as cervical polyps and uterine fibroids, to more serious concerns like cancers and blood disorders.
It is essential to discuss any unusual bleeding with your doctor to identify the cause and to take immediate action.
Frequently Asked Questions about Postmenopausal Bleeding
Is postmenopausal bleeding always a sign of cancer?
No, postmenopausal bleeding isn’t always linked to cancer, but it’s often one of the earliest symptoms of it. That’s why doctors take any bleeding after menopause so seriously.
Other common causes include thinning of the uterine lining (atrophic endometrium), polyps, or side effects associated with hormone therapies. If you experience any unusual symptoms, like postmenopausal bleeding, let your doctor know right away so they can do a thorough workup.
Can hormone therapy cause postmenopausal bleeding?
Yes, some forms of hormone therapy can cause postmenopausal bleeding. Cyclic hormone therapy, where estrogen is taken daily and progesterone is added for only part of the month, can mimic a menstrual cycle and result in light bleeding or spotting at predictable intervals.
Continuous combined hormone therapy, which involves taking estrogen and progesterone together every day, can also cause breakthrough bleeding during the first three to six months of treatment. Symptoms like these should resolve over time as your body adjusts to new hormone levels.
How is postmenopausal bleeding investigated and diagnosed?
Your doctor may recommend a combination of tests based on your symptoms. Transvaginal ultrasound is often the first step used to measure the thickness of the uterine lining and can help your provider look for endometrial cancer and other red flags.
If further evaluation is needed, your doctor might suggest an endometrial biopsy or hysteroscopy. These like these can provide a closer look and confirm whether your bleeding is a result of hyperplasia, cancer, or another condition. These tests are quick and minimally invasive.
Is a single episode of postmenopausal bleeding cause for concern?
Possibly. Even a single episode of postmenopausal bleeding should be reported to your doctor right away. Sometimes, benign issues like minor vaginal tears and shifts in hormones can trigger temporary bleeding that goes away on its own.
Because bleeding can also be a potential warning sign for hyperplasia or early-stage cancer, it should never be ignored. A single occurrence is your body’s way of asking for attention.
Can postmenopausal bleeding be caused by sexual activity?
Yes. Sexual activity can sometimes lead to postmenopausal bleeding, especially if vaginal dryness or atrophy is present. Vaginal tissues become more delicate and fragile after menopause, which can make irritation and small tears more likely. Using lubricants or local hormone therapies like vaginal estrogen can help, but if bleeding persists, tell your doctor.