Table of Contents
- Summary
- Approaches to Treatment for Grade 1 Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma
- Laparoscopic Approach
- Abdominal Approach
- Definitive Treatment and Follow-Up Care for Endometrial Cancer
- A Quick Note on Fertility
- Understanding Your Pathway to Better Health
Summary:
- The primary treatment for Grade 1 Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma involves surgically removing the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, with lymph node removal considered based on patient-specific factors.
- Treatment can be performed using various surgical methods, including minimally invasive laparoscopy, which utilizes small incisions and specialized instruments, or an abdominal incision, depending on individual patient needs.
- After surgery, a pathologist examines the removed tissues to determine the cancer’s final cell type, grade, and stage, which guides any necessary additional treatments, such as radiation or chemotherapy.
- For menstruating women desiring to preserve fertility, progesterone treatment may be offered as a temporary option until family planning is complete, after which surgery may be recommended.
Understanding the approaches to treatment for Grade 1 Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma is necessary for developing effective care strategies. The definitive treatment generally involves the surgical removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, with the potential inclusion of lymph node removal, depending on individual circumstances. Various surgical methods, such as laparoscopic and abdominal approaches, cater to the specific needs of patients, ensuring tailored care that addresses both cancer management and reproductive considerations.
Approaches to Treatment for Grade 1 Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma
The definitive treatment for Grade 1 Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma typically involves surgical removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, with lymph node removal considered in certain cases. This procedure can be performed using various surgical approaches, depending on patient-specific factors.
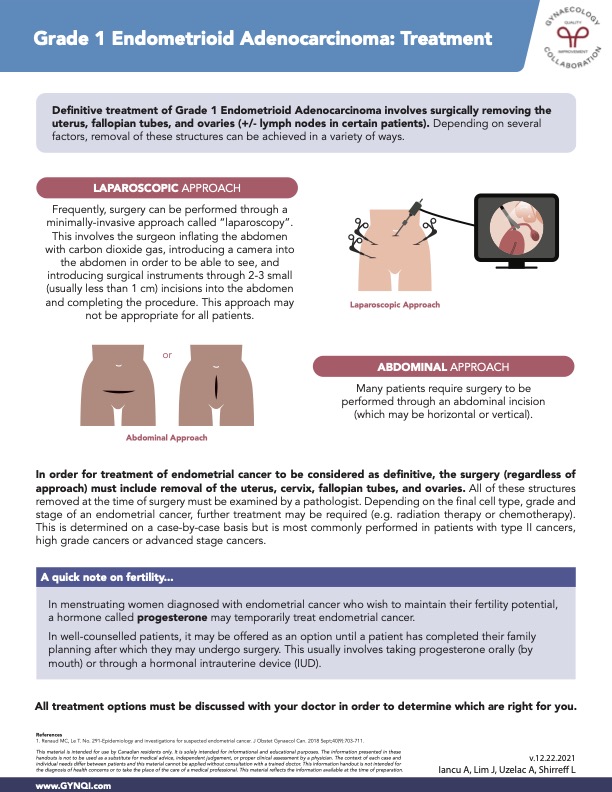
Laparoscopic Approach
Surgery is often performed using a minimally invasive approach called laparoscopy. This technique involves inflating the abdomen with carbon dioxide gas to create a working space, inserting a camera for visualization, and using specialized instruments introduced through two to three small incisions (typically less than 1 cm). However, this approach may not be suitable for all patients.
Abdominal Approach
Some patients require surgery to be performed through an abdominal incision, which may be made horizontally or vertically, depending on individual needs and surgical considerations.
Definitive Treatment and Follow-Up Care for Endometrial Cancer
For endometrial cancer treatment to be considered definitive, surgery must include the removal of the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, regardless of the surgical approach. A pathologist will examine these structures post-surgery. Based on the final cell type, grade, and stage of the cancer, additional treatments, such as radiation or chemotherapy, may be necessary.
These treatments are considered on a case-by-case basis but are most common in patients with type II, high-grade, or advanced-stage cancers.
A Quick Note on Fertility
In menstruating women with endometrial cancer who wish to preserve fertility, treatment with the hormone progesterone may be a temporary option. Progesterone is typically administered either orally or via a hormonal intrauterine device (IUD).
After thorough counseling, eligible patients may consider this approach until they have completed their family planning, after which surgery may be recommended.
Understanding Your Pathway to Better Health
Treatment for Grade 1 Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma typically involves surgical removal of reproductive organs, with minimally invasive and abdominal surgical options available. Further care is guided by pathology results and cancer stage and additional therapies may be needed for high-grade or advanced cancers. Progesterone treatment may offer a temporary fertility-preserving option for patients planning future pregnancies.
It is important to discuss your treatment options with your doctor in order to determine which are right for you.