Table of Contents
- Summary
- What is Vulvodynia?
- Causes of Vulvodynia
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatment of Vulvodynia
- Vulvar Care
- Education
- Drugs
- Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy
- Counselling and Therapy
- Surgery
- A Comprehensive Approach to Managing Vulvodynia
Summary:
- Vulvodynia is characterized by persistent vulvar pain lasting over three months, affecting 8-15% of individuals with a vulva. It can be generalized (constant burning) or localized (triggered by touch).
- The exact cause remains unknown but may involve factors like pelvic floor dysfunction or low estrogen. Symptoms vary and can include burning, stinging, and aching sensations.
- Diagnosis involves clinical exams, including a cotton swab test. Treatment typically includes vulvar care, medications, pelvic floor physiotherapy, and counselling, with surgery considered only if other options fail.
- A holistic approach is crucial for effective management, aiming to reduce pain and improve the quality of life for those affected by vulvodynia.
Vulvodynia is persistent vulvar pain lasting over three months, affecting 8-15% of individuals with a vulva. It can be generalized (constant burning) or localized (triggered by touch), with potential causes including pelvic floor dysfunction or low estrogen. Symptoms vary and include burning and stinging. Diagnosis involves clinical exams, and treatment typically includes vulvar care, medications, pelvic floor physiotherapy, and even counselling, with surgery as a rare option if no other treatments have worked. A comprehensive approach is key for effective management.
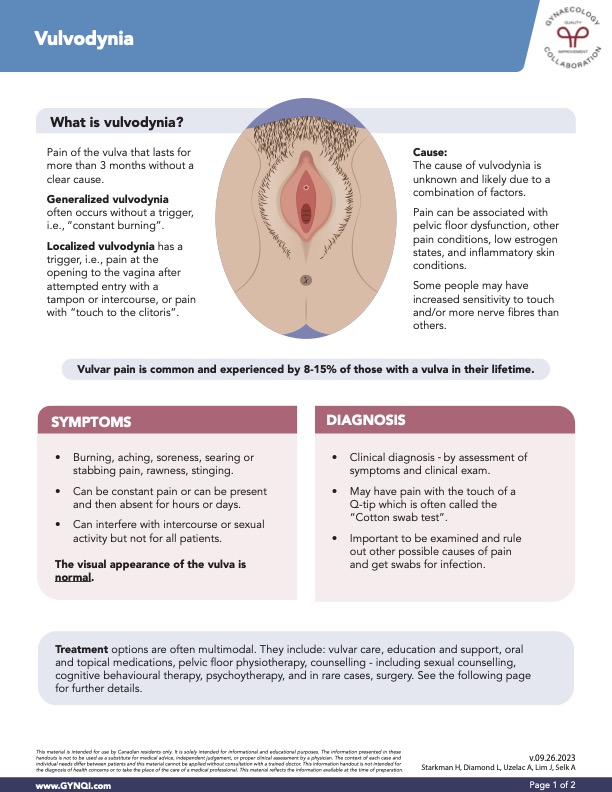
What is Vulvodynia?
Vulvodynia is characterized as pain in your vulva that lasts longer than three months. Unlike vulvar pain that is the result of a condition, vulvodynia doesn’t have a clear cause. Sometimes the pain can prevent you from engaging in activities you enjoy, making it important to seek medical help and explore treatment options.
Generalized vulvodynia: Often occurs without a trigger, and can be described as “constant burning”.
Localized vulvodynia: Has a trigger, which may be pain with a simple touch to the clitoris. Attempted entry with a tampon or with intercourse can also cause pain at the opening of the vagina.
Vulvar pain is common and is experienced by 8-15% of those with a vulva in their lifetime.
Causes of Vulvodynia
Currently, the cause of vulvodynia is unknown and is likely due to a combination of factors. Pain can be caused due to:
- Pelvic floor dysfunction
- Low estrogen states
- Inflammatory skin conditions
- Other pain conditions
Some people may have increased sensitivity to touch or more nerve fibres than others, contributing to vulvodynia.
Symptoms
Vulvodynia can present in a few different ways. Painful sensations may be constant, or can fluctuate over hours or days, interfering with sexual activity and your day-to-day life.
Even though your vulva may appear normal, speak to your doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Burning
- Aching
- Soreness
- Searing or stabbing pain
- Rawness
- Stinging
Diagnosis
Vulvodynia is diagnosed with a clinical exam, with an assessment of your symptoms. It is important to be examined to rule out other possible causes of pain.
A “cotton swab test” can also determine where and if you have pain with pressure-point testing. Your doctor will brush a cotton swab gently over parts of your vulva and ask if there is pain on contact. This is helpful for diagnosing localized pain at the opening of your urethra and vagina.
Ask your doctor to swab for any possible infections.
Treatment of Vulvodynia
Treatment options often involve a combination of approaches, including vulvar care, education and support, oral and topical medications, pelvic floor physiotherapy, and various counselling options like sexual counselling, cognitive behavioral therapy, and psychotherapy. In rare cases, surgery may be required.
Vulvar Care
The main aspect of vulvar care is reducing irritation to the vulva and vagina and trying to bring as much breathability to clothing options as possible.
Tips include:
- Avoiding soaps, detergents, fabric softeners, and products with scents and fragrances
- Using unscented lubricants for intercourse or sexual activities
- Avoiding wearing tight clothing, including tight underwear against the vulva
Education
Educating yourself on all aspects of vulvodynia is important. Be sure to ask your doctor any questions you have, and see if they have any suggestions for support networks outside the doctor’s office.
Drugs
Managing vulvodynia often involves various treatment options, particularly medications. Oral antidepressants and anticonvulsants can also relieve pain, while topical lidocaine may be prescribed to provide comfort.
Oral medications: Antidepressants and anticonvulsants have been shown to have pain-relieving properties and are often used in many chronic pain conditions.
Treatment may include medications like:
- Tricyclic medications–amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine and desipramine
- Gabapentin, pregabalin, duloxetine and venlafaxine
Topical medications: Many oral drugs are taken in pill form but sometimes medications such as tricyclics and gabapentin are compounded into creams to apply to the vulva. Topical lidocaine 2-5% is sometimes used for relief, though topical treatments can be irritating and sometimes worsen the pain.
Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy
Pelvic floor physiotherapy is an evidence-based specialized treatment that targets the muscles and connective tissues of the pelvic floor to alleviate issues like pelvic pain, incontinence, and sexual dysfunction.
Pelvic floor physio includes:
- Exercises to retrain the pelvic floor muscles
- Manual therapy
- Biofeedback–a mind-body therapy to help create conscious changes in involuntary functions
- Education and awareness on retraining your pelvic floor, helping improve muscle function and overall quality of life
Counselling and Therapy
As part of a holistic approach to treatment, counselling is essential for managing vulvodynia.
Sexual counselling can help if you are experiencing sexual problems and can include individual or couples therapy.
Cognitive behavioural therapy and psychological counselling has been shown to be helpful in reducing anxiety by rewiring how thoughts feed into the pain symptom cycle.
Surgery
In extreme cases, surgery may be required. A vestibulectomy is a type of surgery that removes tissue from your vaginal opening. This is performed when the pain is localized and other treatment methods haven’t worked.
A Comprehensive Approach to Managing Vulvodynia
Vulvodynia is a complex condition characterized by persistent vulvar pain lasting over three months. This condition impacts 8-15% of individuals with a vulva, with the overall cause currently unknown. Effective management often requires a well-rounded approach that includes vulvar care and medications, with surgery as a last-step option only when other treatments have failed. Addressing vulvodynia with a holistic approach can significantly improve your quality of life after your initial diagnosis.