Table of Contents
- Summary
- What Are Vasomotor Symptoms?
- Non-Hormonal Treatment Options
- Estrogen Therapy
- Progesterone Therapy
- Combination Menopause Hormone Therapy
- Choosing the Right Treatment Plan for Your Needs
Summary:
- Vasomotor symptoms (VMS), such as hot flashes and night sweats, are common during menopause due to fluctuating hormone levels, particularly a decrease in estrogen.
- Non-hormonal treatments, including SSRIs and SNRIs like Citalopram and Gabapentin, offer alternatives to hormone therapy and help reduce VMS frequency and intensity.
- Hormone therapies, including estrogen and progesterone, are effective in managing VMS and can be tailored to individual needs
- Combination therapy addresses certain cancer risks and also can eliminate the need to take a second medication.
Vasomotor symptoms (VMS), such as hot flashes and night sweats, commonly occur during menopause due to hormonal shifts, particularly decreased estrogen. These symptoms can disrupt daily life, prompting many to seek relief through treatments.
Options for treatment include non-hormonal therapies like SSRIs and SNRIs, as well as hormone-based treatments such as estrogen, progesterone, and combination therapies, each offering tailored solutions for managing VMS.
What Are Vasomotor Symptoms?
Vasomotor symptoms (VMS) are sensations of sudden, intense heat, often associated with menopause or hormonal changes, and include hot flashes and night sweats. VMS occurs as hormonal levels fluctuate, especially around menopause when estrogen levels decrease.
Since vasomotor symptoms can disrupt daily life and sleep quality, many people seek treatments to manage their symptoms from a variety of options.
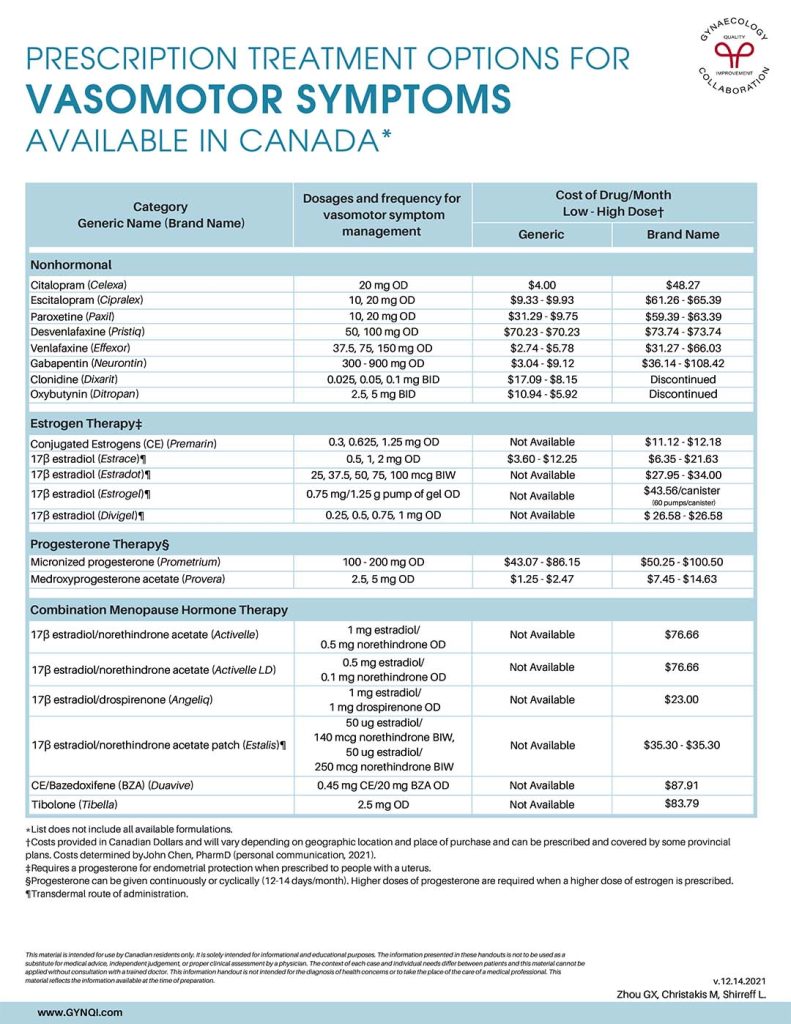
Non-Hormonal Treatment Options
It has been found that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a potentially effective alternative treatment to hormone replacement therapy. Medications like Citalopram and Gabapentin have been shown to reduce the frequency and/or severity of hot flashes in menopausal and postmenopausal women.
The dosages, frequency, and cost for the generic and brand-name non-hormonal medications are listed in the table below:
Estrogen Therapy
Hormone therapy is the most effective treatment for vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and other symptoms of menopause. Estrogen plays a powerful role in regulating many nerve pathways throughout the brain and central nervous system. Changes in estrogen levels during menopause can disrupt these pathways, causing your body to release higher amounts of other hormones that affect the brain’s thermostat.
Estrogen therapy works to restore some of that balance, helping to relieve hot flashes and reduce discomfort for many women.
Progesterone Therapy
As progesterone levels decrease after menopause, using progesterone therapy can be an effective treatment for hot flashes and night sweats, and may also be effective in protecting against cognitive decline.
Progesterone also protects the lining of the uterus from developing cancer or pre-cancer cells.
Combination Menopause Hormone Therapy
Combining estrogens with progestogens is recommended to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer associated with estrogen use. Some hormone therapy products offer a convenient combination of both estrogen and progesterone, eliminating the need for additional medication for individuals with a uterus.
Choosing the Right Treatment Plan For Your Needs
Vasomotor symptoms (VMS) like hot flashes and night sweats are common during menopause due to hormonal shifts. Treatment options vary: non-hormonal choices like SSRIs and SNRIs offer relief without hormones, while estrogen therapy is the most effective for managing VMS.
Progesterone therapy aids in symptom relief and protects uterine health, and combination therapies offer both estrogen and progesterone benefits, reducing cancer risks associated with estrogen alone.
With diverse options, individuals can choose treatments that best suit their needs and health goals.



