Complete Guide to Heavy Periods & Iron Deficiency
1 in 4 people with a uterus experience heavy periods. Heavy periods (or Heavy Menstrual Bleeding) refers to abnormally heavy or longer than normal periods. Heavy menstrual bleeding can lead to Iron Deficiency Anemia in some people. Both of these conditions can negatively affect a person’s physical, emotional and social well-being.
We are pleased to provide resources below that were created by medical experts. Below, you’ll find information on the treatments for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding and Iron Deficiency Anemia.
What Is Heavy Menstrual Bleeding?
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (HMB) refers to abnormally heavy or longer than normal periods. It can lead to significant disruptions in people’s daily activities and lifestyle, impacting their physical, emotional and social well-being.
People with heavy periods may also suffer from Iron Deficiency Anemia, with symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness or shortness of breath.
Learn more about Iron Deficiency here.

Heavy Period Symptoms
Do any of these symptoms apply to you? If so, you may suffer from Heavy Menstrual Bleeding.

Having to change sanitary protection during the night

Feeling faint or breathless during a period

Organizing social activities or clothing around bleeding


Diagnosing Heavy Periods
- Blood Tests: These will include complete blood count (CBC) and ferritin. These tests will help diagnose iron-deficient anemia.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: An external probe on your lower abdomen provides images of your pelvic structure. A transvaginal ultrasound may be completed at the same time, with your consent. In a transvaginal ultrasound, a probe is inserted into the vagina to better delineate the female reproductive organs.
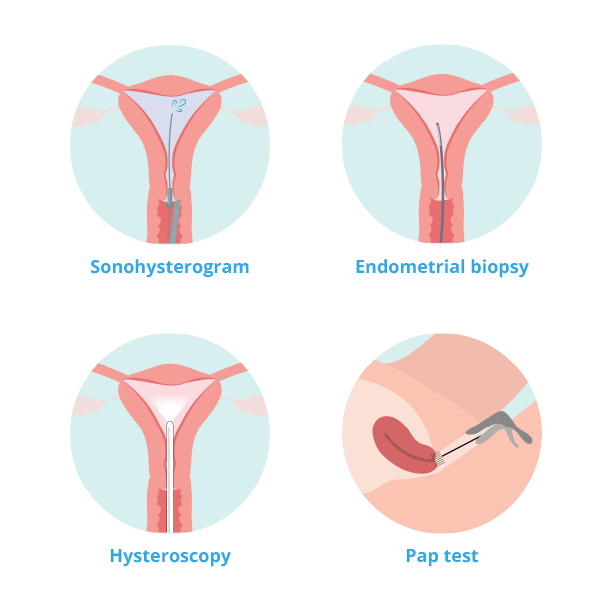
- Sonohysterogram: A procedure that typically involves insertion of a speculum, followed by injection of fluid through the cervix and into the uterine cavity. An ultrasound is completed at the same time, which provides a more detailed assessment of your uterus. Specifically, this test will tell your doctor about whether there are any structures in the cavity of your uterus contributing to post-menopausal bleeding.
- Endometrial Biopsy: A short office procedure during which a speculum is inserted into the vagina and a small pipelle is placed through the opening of the cervix, and into the uterus to take a sample of the lining of the uterus. Some people find this procedure uncomfortable and cannot tolerate having it done in the office. Your doctor may recommend a short procedure in the operating room under anesthesia instead.
- Hysteroscopy: This procedure, usually done in the operating room, involves a small camera being inserted through the vagina, cervix, and into the uterus. Fluid is used to expand the cavity of the uterus. Hysteroscopy will let your doctor directly see the inside of the uterus. Your doctor may also take a sample of the tissue under direct visualization.
- Pap Test: An office procedure that involves a speculum examination. Your doctor will use a small brush to gently sample cells from the cervix so they can be checked for any precancer or cancer changes.
Medical Treatment Options

Non-Steriodal Anti-Inflammatory
- 20-50% reduction in menstrual bleeding
- Reduction in menstrual cramps and/or pain during period in up to 70% of patients
- No
- Can be used in combination with other medical treatments and while awaiting further investigations into causes of HMB
- Indigestion
- Worsening of athsma
- Gastritis
- Peptic ulcers

Tranexamic Acid
- 40-59% reduction in menstrual bleeding
- No
- TXA can be used in combination with other medical treatments and while awaiting further investigations into causes of HMB
- TXA is not used for treating associated menstrual cramps or painful periods
- Indigestion
- Diarrhea
- Headaches
- Leg cramps
Levonorgestrel IUD
- 70-97% reduction in menstrual bleeding
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) experienced by 20-80% of patients after 1 year of use
- LNG-IUS use is associated with reduction in menstrual cramps and/or pain during period
- Yes
- May not be ideal for patients with a distorted uterine cavity, such as those with multiple fibroids that are positioned near or in the uterine cavity
- Irregular bleeding during the first 6 months
- Breast tenderness
- Acne
- Cramping
- Headaches
Combined Hormonal Contraceptive
- 20-50% reduction in menstrual bleeding
- CHC use associated with reduction in pain during period (dysmenorrhea) and pre-menstrual symptoms
CHCs may also provide menstrual regularity
- Yes
- CHCs have no impact on future fertility
- Breast tenderness
- Mood changes
- Fluid retention
- Breakthrough bleeding
Progestin (Cyclic Oral)
- Up to 87% reduction in menstrual bleeding
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) experienced by 20-80% of patients after 1 year of use
- LNG-IUS use is associated with reduction in menstrual cramps and/or pain during period
- No
- May reduce ability to conceive while on treatment (may not be appropriate for those trying to conceive)
- Breast tenderness
- Mood changes
- Bloating
- Acne
- Headaches
- Weight gain
Progestin (Injectable)
- 70-97% reduction in menstrual bleeding
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) experienced by 20-80% of patients after 1 year of use
- LNG-IUS use is associated with reduction in menstrual cramps and/or pain during period
- Yes
- Delay in return to fertility
- Irregular bleeding
- Breast tenderness
- Weight gain
- Mood changes
- Decreased bone mineral density
GnRH Agonists
- Amenorrhea experienced by up to 89% of patients within 3-4 weeks of first injection
- No
- May not be appropriate for those trying to conceive
- Hypoestrogenic symptoms (hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness)
- Bone pain
- Loss of bone mineral density
- Mood changes
GnRH Antagonists (Access handout here)
What Is Iron Deficiency?
Iron is an important component of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen around the body.
When your body does not have enough iron, your hemoglobin levels can drop below normal, and your organs are unable to get the right amount of oxygen they require. This condition is known as Iron Deficiency Anemia.
It is the most common form of anemia. Iron Deficiency can lead to many symptoms and impair your ability to do normal daily activities.

Iron Deficiency Anemia Symptoms
If any of the following symptoms apply to you, you may have Iron Deficiency or Iron Deficiency Anemia.








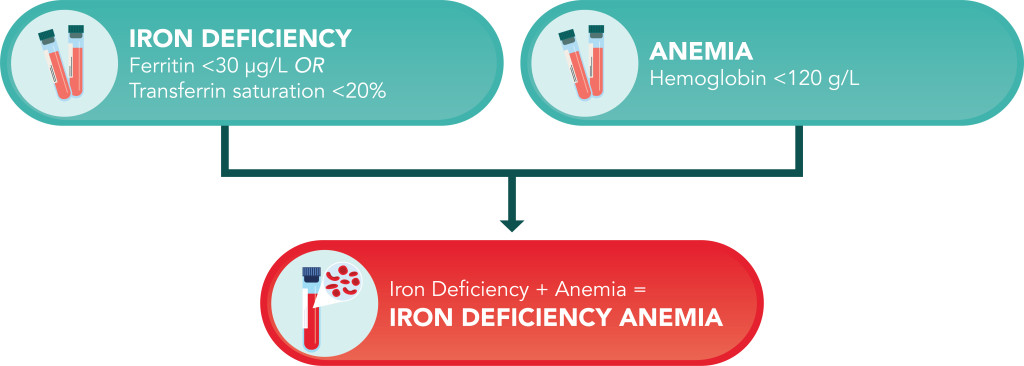
Conditions for Diagnosis
- Ferritin <30 ug/L OR Transferrin saturation <20%
- Hemoglobin <120 g/L
- The presence of both iron deficiency and anemia
Medical Treatment Options
Oral Iron
- Over the counter (no prescription required)
- Available as pills, capsules, drops, and extended release tablets
- Dosing varies depending on iron preparation and individual patient considerations
- Dark stools
- Stomach discomfort
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
Intravenous Iron
- Rapidly delivers iron into the bloodstream
- Subsidized by many individual healthcare plans
- Notify your doctor about any medications you take, and if you are in the first trimester of pregnancy, have had reactions to iron injections or infusions in the past, have liver disease or abnormal liver function test results, or have any new or ongoing infections.
- Headaches
- Muscle or joint pain
- Feeling sick or vomiting
- Changes in taste (i.e. metallic)
- Changes in blood pressure or pulse
- Irritation at injection site
Preparing for Surgery
It is ideal for people to go into surgery with a hemoglobin level
greater than 120 g/L.
If You Are Preparing for Surgery
Importance of Treating Anemia
Frequently Asked Questions About Heavy Periods & Iron Deficiency Anemia
Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) is defined as excessive blood loss that interferes with daily activities. Periods may last longer than 7 days or you might need to change out your pad or tampon frequently throughout the day.
HMB can be caused by hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids, polyps, endometriosis, or bleeding disorders. It can also happen without any identifiable cause.
Let your doctor know right away if your bleeding is heavy enough to disrupt daily activities, if you have severely painful periods, or pass large clots. You may be struggling with a condition like fibroids or endometriosis.
Pharmacological options include hormonal treatments like birth control pills, progesterone, and IUDs. For patients who don’t want to or can’t take hormones, tranexamic acid and NSAIDs may provide relief.
Hormonal treatments are highly effective at treating HMB in many patients. They help to regulate periods and reduce the volume of blood loss.
Yes. Non-hormonal options include medications like tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss and NSAIDs to manage pain and inflammation.
Yes! Many women manage HMB effectively with medication or lifestyle changes until menopause arrives. Surgery is only considered for cases where other treatments are not successful.
Potential side effects can vary, but typically include nausea, changes in weight, or spotting. Your provider will discuss these with you before treatment.
Results vary, but many patients report a noticeable improvement within one to three months of starting treatment. Your provider will monitor your progress and adjust as needed along the way.
If medications are ineffective, your doctor might recommend minimally invasive procedures or surgery to help address the cause of your bleeding. Your doctor can help you understand if these options are right for you.